Higher Efficiency.
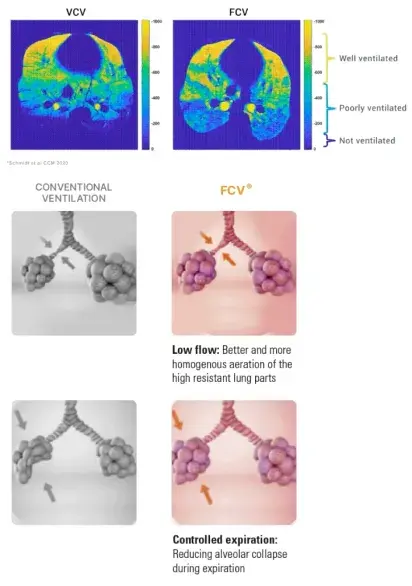
Conventional ventilation uses relatively high gas flows, requiring high pressure to reach obstructive lung parts. With FCV® lower flows are used that range typically between 8 and 16 L/Min to adequately ventilate a patient.
At lower flows , gas is better able to reach the lung units that have higher resistance and the dependent lung parts that have better perfusion.
A passive expiration results in an abrupt deflation especially in the low compliant lung units. By controlling the expiration flow, FCV® mantains airway pressure and keeps gas flowing in the alveoli longer.
Thus, FCV® can avoid or delay airway and alveaolar collapse, and thereby avoid atelectasis while improving gas exchange.
Together, FCV® results in a higher efficient ventilation as compared to conventional ventilation techniques. These properties of FCV® have been demonstrated in multiple scientific studies.
Benefits of Higher Efficiency.
The following benefits as compared to Volume Controlled Ventilation (VCV) and Pressure Controlled Ventilation (PCV) with conventional endotracheal tubes may be expected while ventilating patients in FCV® mode with ultrathin Tritube®.
- Keeps the lung open by controlling the full ventilation cycle.
- Results in better lung recruitment as compared to VCV and PCV 3, 4, 10, 13, 18, 26.
- Results in better aeration of the lungs as compared to VCV and PCV 3, 4, 10, 13, 18, 19, 26.
- Provides higher efficient ventilation as compared to VCV, and PCV, evidenced by improved oxygenation and CO2 removal 1-6, 10, 13, 15, 16, 18, 26.
- Reduces atelectasis in dependent lung parts as compared to VCV in porcine ARDS and morbidly obese patients 10, 19.
- Evone® allows individual optimization of ventilation settings based on compliance 3, 7, 8, 13, 14, 17.